Python (programming language)
 | |
| Paradigm | Multi-paradigm: object-oriented,[1] procedural (imperative), functional, structured, reflective |
|---|---|
| Designed by | Guido van Rossum |
| Developer | Python Software Foundation |
| First appeared | 20 February 1991[2] |
| Stable release | |
| Typing discipline | duck, dynamic, strong;[3] optional type annotations (since 3.5, but those hints are ignored, except with unofficial tools)[4] |
| OS | |
| License | Python Software Foundation License |
| Filename extensions | .py, .pyw, .pyz,[10] .pyi, .pyc, .pyd |
| Website | python.org |
| Major implementations | |
| CPython, PyPy, Stackless Python, MicroPython, CircuitPython, IronPython, Jython | |
| Dialects | |
| Cython, RPython, Starlark[11] | |
| Influenced by | |
| ABC,[12] Ada,[13] ALGOL 68,[14] APL,[15] C,[16] C++,[17] CLU,[18] Dylan,[19] Haskell,[20][15] Icon,[21] Lisp,[22] Modula-3,[14][17] Perl,[23] Standard ML[15] | |
| Influenced | |
| Apache Groovy, Boo, Cobra, CoffeeScript,[24] D, F#, GDScript, Go, JavaScript,[25][26] Julia,[27] Mojo,[28] Nim, Ring,[29] Ruby,[30] Swift[31] | |
| |
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language and object oriented programming. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation.[32]
Python is dynamically typed and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library.[33][34]
Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language and first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0.[35] Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of Python 2.[36]
Python consistently ranks as one of the most popular programming languages, and has gained widespread use in the machine learning community.[37][38][39][40]
History
[edit]
Python was invented in the late 1980s[41] by Guido van Rossum at Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica (CWI) in the Netherlands as a successor to the ABC programming language, which was inspired by SETL,[42] capable of exception handling and interfacing with the Amoeba operating system.[12] Its implementation began in December 1989.[43] Van Rossum shouldered sole responsibility for the project, as the lead developer, until 12 July 2018, when he announced his "permanent vacation" from his responsibilities as Python's "benevolent dictator for life" (BDFL), a title the Python community bestowed upon him to reflect his long-term commitment as the project's chief decision-maker[44] (he has since come out of retirement and is self-titled "BDFL-emeritus"). In January 2019, active Python core developers elected a five-member Steering Council to lead the project.[45][46]
Python 2.0 was released on 16 October 2000, with many major new features such as list comprehensions, cycle-detecting garbage collection, reference counting, and Unicode support.[47] Python 3.0 was released on 3 December 2008, with many of its major features backported to Python 2.6.x[48] and 2.7.x. Releases of Python 3 include the 2to3 utility, which automates the translation of Python 2 code to Python 3.[49]
Python 2.7's end-of-life was initially set for 2015, then postponed to 2020 out of concern that a large body of existing code could not easily be forward-ported to Python 3.[50][51] No further security patches or other improvements will be released for it.[52][53] Currently only 3.9 and later are supported (2023 security issues were fixed in e.g. 3.7.17, the final 3.7.x release[54]). While Python 2.7 and older is officially unsupported, a different unofficial Python implementation, PyPy, continues to support Python 2, i.e. "2.7.18+" (plus 3.10), with the plus meaning (at least some) "backported security updates".[55]
In 2021 (and again twice in 2022, and in September 2024 for Python 3.12.6 down to 3.8.20), security updates were expedited, since all Python versions were insecure (including 2.7[56]) because of security issues leading to possible remote code execution[57] and web-cache poisoning.[58] In 2022, Python 3.10.4 and 3.9.12 were expedited[59] and 3.8.13, because of many security issues.[60] When Python 3.9.13 was released in May 2022, it was announced that the 3.9 series (joining the older series 3.8 and 3.7) would only receive security fixes in the future.[61] On 7 September 2022, four new releases were made due to a potential denial-of-service attack: 3.10.7, 3.9.14, 3.8.14, and 3.7.14.[62][63]
Every Python release since 3.5 has added some syntax to the language. 3.10 added the | union type operator[64] and the match and case keywords (for structural pattern matching statements). 3.11 expanded exception handling functionality. Python 3.12 added the new keyword type. Notable changes in 3.11 from 3.10 include increased program execution speed and improved error reporting.[65] Python 3.11 claims to be between 10 and 60% faster than Python 3.10, and Python 3.12 adds another 5% on top of that. It also has improved error messages, and many other changes.
Python 3.13 introduces more syntax for types, a new and improved interactive interpreter (REPL), featuring multi-line editing and color support; an incremental garbage collector (producing shorter pauses for collection in programs with a lot of objects, and addition to the improved speed in 3.11 and 3.12), and an experimental just-in-time (JIT) compiler (such features, can/needs to be enabled specifically for the increase in speed),[66] and an experimental free-threaded build mode, which disables the global interpreter lock (GIL), allowing threads to run more concurrently, that latter feature enabled with python3.13t or python3.13t.exe.
Python 3.13 introduces some change in behavior, i.e. new "well-defined semantics", fixing bugs (plus many removals of deprecated classes, functions and methods, and removed some of the C API and outdated modules): "The [old] implementation of locals() and frame.f_locals is slow, inconsistent and buggy [and it has] has many corner cases and oddities. Code that works around those may need to be changed. Code that uses locals() for simple templating, or print debugging, will continue to work correctly."[67]
Since 7 October 2024[update], Python 3.13 is the latest stable release, and 3.13 and 3.12 are the only versions with active (as opposed to just security) support and Python 3.9 is the oldest supported version of Python (albeit in the 'security support' phase), due to Python 3.8 reaching end-of-life.[68] Starting with 3.13, it and later versions have 2 years of full support (up from one and a half); followed by 3 years of security support (for same total support as before).
Some (more) standard library modules and many deprecated classes, functions and methods, will be removed in Python 3.15 or 3.16.[69][70]
Python 3.14 (now in alpha 1)[71] has changes for annotations, with PEP 649 "[preserving] nearly all existing behavior of annotations from stock semantics".[72]
Design philosophy and features
[edit]Python is a multi-paradigm programming language. Object-oriented programming and structured programming are fully supported, and many of their features support functional programming and aspect-oriented programming (including metaprogramming[73] and metaobjects).[74] Many other paradigms are supported via extensions, including design by contract[75][76] and logic programming.[77] Python is known as a glue language,[78] able to work very well with many other languages with ease of access.
Python uses dynamic typing and a combination of reference counting and a cycle-detecting garbage collector for memory management.[79] It uses dynamic name resolution (late binding), which binds method and variable names during program execution.
Its design offers some support for functional programming in the Lisp tradition. It has filter,mapandreduce functions; list comprehensions, dictionaries, sets, and generator expressions.[80] The standard library has two modules (itertools and functools) that implement functional tools borrowed from Haskell and Standard ML.[81]
Its core philosophy is summarized in the Zen of Python (PEP 20), which includes aphorisms such as:[82]
- Beautiful is better than ugly.
- Explicit is better than implicit.
- Simple is better than complex.
- Complex is better than complicated.
- Readability counts.
However, Python features regularly violate these principles and have received criticism for adding unnecessary language bloat.[83] Responses to these criticisms are that the Zen of Python is a guideline rather than a rule.[84] The addition of some new features had been so controversial that Guido van Rossum resigned as Benevolent Dictator for Life following vitriol over the addition of the assignment expression operator in Python 3.8.[85][86]
Nevertheless, rather than building all of its functionality into its core, Python was designed to be highly extensible via modules. This compact modularity has made it particularly popular as a means of adding programmable interfaces to existing applications. Van Rossum's vision of a small core language with a large standard library and easily extensible interpreter stemmed from his frustrations with ABC, which espoused the opposite approach.[41]
Python claims to strive for a simpler, less-cluttered syntax and grammar while giving developers a choice in their coding methodology. In contrast to Perl's "there is more than one way to do it" motto, Python embraces a "there should be one—and preferably only one—obvious way to do it." philosophy.[82] In practice, however, Python provides many ways to achieve the same task. There are, for example, at least three ways to format a string literal, with no certainty as to which one a programmer should use.[87] Alex Martelli, a Fellow at the Python Software Foundation and Python book author, wrote: "To describe something as 'clever' is not considered a compliment in the Python culture."[88]
Python's developers usually strive to avoid premature optimization and reject patches to non-critical parts of the CPython reference implementation that would offer marginal increases in speed at the cost of clarity.[89] Execution speed can be improved by moving speed-critical functions to extension modules written in languages such as C, or by using a just-in-time compiler like PyPy. It is also possible to cross-compile to other languages, but it either doesn't provide the full speed-up that might be expected, since Python is a very dynamic language, or a restricted subset of Python is compiled, and possibly semantics are slightly changed.[90]
Python's developers aim for it to be fun to use. This is reflected in its name—a tribute to the British comedy group Monty Python[91]—and in occasionally playful approaches to tutorials and reference materials, such as the use of the terms "spam" and "eggs" (a reference to a Monty Python sketch) in examples, instead of the often-used "foo" and "bar".[92][93] A common neologism in the Python community is pythonic, which has a wide range of meanings related to program style. "Pythonic" code may use Python idioms well, be natural or show fluency in the language, or conform with Python's minimalist philosophy and emphasis on readability. Code that is difficult to understand or reads like a rough transcription from another programming language is called unpythonic.[94]
Syntax and semantics
[edit]

Python is meant to be an easily readable language. Its formatting is visually uncluttered and often uses English keywords where other languages use punctuation. Unlike many other languages, it does not use curly brackets to delimit blocks, and semicolons after statements are allowed but rarely used. It has fewer syntactic exceptions and special cases than C or Pascal.[95]
Indentation
[edit]Python uses whitespace indentation, rather than curly brackets or keywords, to delimit blocks. An increase in indentation comes after certain statements; a decrease in indentation signifies the end of the current block.[96] Thus, the program's visual structure accurately represents its semantic structure.[97] This feature is sometimes termed the off-side rule. Some other languages use indentation this way; but in most, indentation has no semantic meaning. The recommended indent size is four spaces.[98]
Statements and control flow
[edit]Python's statements include:
- The assignment statement, using a single equals sign
= - The
ifstatement, which conditionally executes a block of code, along withelseandelif(a contraction of else-if) - The
forstatement, which iterates over an iterable object, capturing each element to a local variable for use by the attached block - The
whilestatement, which executes a block of code as long as its condition is true - The
trystatement, which allows exceptions raised in its attached code block to be caught and handled byexceptclauses (or new syntaxexcept*in Python 3.11 for exception groups[99]); it also ensures that clean-up code in afinallyblock is always run regardless of how the block exits - The
raisestatement, used to raise a specified exception or re-raise a caught exception - The
classstatement, which executes a block of code and attaches its local namespace to a class, for use in object-oriented programming - The
defstatement, which defines a function or method - The
withstatement, which encloses a code block within a context manager (for example, acquiring a lock before it is run, then releasing the lock; or opening and closing a file), allowing resource-acquisition-is-initialization (RAII)-like behavior and replacing a common try/finally idiom[100] - The
breakstatement, which exits a loop - The
continuestatement, which skips the rest of the current iteration and continues with the next - The
delstatement, which removes a variable—deleting the reference from the name to the value, and producing an error if the variable is referred to before it is redefined - The
passstatement, serving as a NOP, syntactically needed to create an empty code block - The
assertstatement, used in debugging to check for conditions that should apply - The
yieldstatement, which returns a value from a generator function (and also an operator); used to implement coroutines - The
returnstatement, used to return a value from a function - The
importandfromstatements, used to import modules whose functions or variables can be used in the current program - The
matchandcasestatements, an analog of the switch statement construct, that compares an expression against one or more cases as a control-of-flow measure.
The assignment statement (=) binds a name as a reference to a separate, dynamically allocated object. Variables may subsequently be rebound at any time to any object. In Python, a variable name is a generic reference holder without a fixed data type; however, it always refers to some object with a type. This is called dynamic typing—in contrast to statically-typed languages, where each variable may contain only a value of a certain type.
Python does not support tail call optimization or first-class continuations, and, according to Van Rossum, it never will.[101][102] However, better support for coroutine-like functionality is provided by extending Python's generators.[103] Before 2.5, generators were lazy iterators; data was passed unidirectionally out of the generator. From Python 2.5 on, it is possible to pass data back into a generator function; and from version 3.3, it can be passed through multiple stack levels.[104]
Expressions
[edit]Python's expressions include:
- The
+,-, and*operators for mathematical addition, subtraction, and multiplication are similar to other languages, but the behavior of division differs. There are two types of divisions in Python: floor division (or integer division)//and floating-point/division.[105] Python uses the**operator for exponentiation. - Python uses the
+operator for string concatenation. Python uses the*operator for duplicating a string a specified number of times. - The
@infix operator. It is intended to be used by libraries such as NumPy for matrix multiplication.[106][107] - The syntax
:=, called the "walrus operator", was introduced in Python 3.8. It assigns values to variables as part of a larger expression.[108] - In Python,
==compares by value. Python'sisoperator may be used to compare object identities (comparison by reference), and comparisons may be chained—for example,a <= b <= c. - Python uses
and,or, andnotas Boolean operators. - Python has a type of expression named a list comprehension, and a more general expression named a generator expression.[80]
- Anonymous functions are implemented using lambda expressions; however, there may be only one expression in each body.
- Conditional expressions are written as
x if c else y[109] (different in order of operands from thec ? x : yoperator common to many other languages). - Python makes a distinction between lists and tuples. Lists are written as
[1, 2, 3], are mutable, and cannot be used as the keys of dictionaries (dictionary keys must be immutable in Python). Tuples, written as(1, 2, 3), are immutable and thus can be used as keys of dictionaries, provided all of the tuple's elements are immutable. The+operator can be used to concatenate two tuples, which does not directly modify their contents, but produces a new tuple containing the elements of both. Thus, given the variabletinitially equal to(1, 2, 3), executingt = t + (4, 5)first evaluatest + (4, 5), which yields(1, 2, 3, 4, 5), which is then assigned back tot—thereby effectively "modifying the contents" oftwhile conforming to the immutable nature of tuple objects. Parentheses are optional for tuples in unambiguous contexts.[110] - Python features sequence unpacking where multiple expressions, each evaluating to anything that can be assigned (to a variable, writable property, etc.) are associated in an identical manner to that forming tuple literals—and, as a whole, are put on the left-hand side of the equal sign in an assignment statement. The statement expects an iterable object on the right-hand side of the equal sign that produces the same number of values as the provided writable expressions; when iterated through them, it assigns each of the produced values to the corresponding expression on the left.[111]
- Python has a "string format" operator
%that functions analogously toprintfformat strings in C—e.g."spam=%s eggs=%d" % ("blah", 2)evaluates to"spam=blah eggs=2". In Python 2.6+ and 3+, this was supplemented by theformat()method of thestrclass, e.g."spam={0} eggs={1}".format("blah", 2). Python 3.6 added "f-strings":spam = "blah"; eggs = 2; f'spam={spam} eggs={eggs}'.[112] - Strings in Python can be concatenated by "adding" them (with the same operator as for adding integers and floats), e.g.
"spam" + "eggs"returns"spameggs". If strings contain numbers, they are added as strings rather than integers, e.g."2" + "2"returns"22". - Python has various string literals:
- Delimited by single or double quotes; unlike in Unix shells, Perl, and Perl-influenced languages, single and double quotes work the same. Both use the backslash (
\) as an escape character. String interpolation became available in Python 3.6 as "formatted string literals".[112] - Triple-quoted (beginning and ending with three single or double quotes), which may span multiple lines and function like here documents in shells, Perl, and Ruby.
- Raw string varieties, denoted by prefixing the string literal with
r. Escape sequences are not interpreted; hence raw strings are useful where literal backslashes are common, such as regular expressions and Windows-style paths. (Compare "@-quoting" in C#.)
- Delimited by single or double quotes; unlike in Unix shells, Perl, and Perl-influenced languages, single and double quotes work the same. Both use the backslash (
- Python has array index and array slicing expressions in lists, denoted as
a[key],a[start:stop]ora[start:stop:step]. Indexes are zero-based, and negative indexes are relative to the end. Slices take elements from the start index up to, but not including, the stop index. The third slice parameter, called step or stride, allows elements to be skipped and reversed. Slice indexes may be omitted—for example,a[:]returns a copy of the entire list. Each element of a slice is a shallow copy.
In Python, a distinction between expressions and statements is rigidly enforced, in contrast to languages such as Common Lisp, Scheme, or Ruby. This leads to duplicating some functionality. For example:
- List comprehensions vs.
for-loops - Conditional expressions vs.
ifblocks - The
eval()vs.exec()built-in functions (in Python 2,execis a statement); the former is for expressions, the latter is for statements
Statements cannot be a part of an expression—so list and other comprehensions or lambda expressions, all being expressions, cannot contain statements. A particular case is that an assignment statement such as a = 1 cannot form part of the conditional expression of a conditional statement.
Methods
[edit]Methods on objects are functions attached to the object's class; the syntax instance.method(argument) is, for normal methods and functions, syntactic sugar for Class.method(instance, argument). Python methods have an explicit self parameter to access instance data, in contrast to the implicit self (or this) in some other object-oriented programming languages (e.g., C++, Java, Objective-C, Ruby).[113] Python also provides methods, often called dunder methods (due to their names beginning and ending with double-underscores), to allow user-defined classes to modify how they are handled by native operations including length, comparison, in arithmetic operations and type conversion.[114]
Typing
[edit]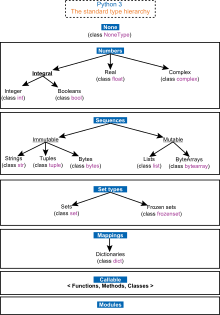
Python uses duck typing and has typed objects but untyped variable names. Type constraints are not checked at compile time; rather, operations on an object may fail, signifying that it is not of a suitable type. Despite being dynamically typed, Python is strongly typed, forbidding operations that are not well-defined (for example, adding a number to a string) rather than silently attempting to make sense of them.
Python allows programmers to define their own types using classes, most often used for object-oriented programming. New instances of classes are constructed by calling the class (for example, SpamClass() or EggsClass()), and the classes are instances of the metaclass type (itself an instance of itself), allowing metaprogramming and reflection.
Before version 3.0, Python had two kinds of classes (both using the same syntax): old-style and new-style;[115] current Python versions only support the semantics of the new style.
Python supports optional type annotations.[4][116] These annotations are not enforced by the language, but may be used by external tools such as mypy to catch errors.[117][118] Mypy also supports a Python compiler called mypyc, which leverages type annotations for optimization.[119]
| Type | Mutability | Description | Syntax examples |
|---|---|---|---|
bool
|
immutable | Boolean value | TrueFalse
|
bytearray
|
mutable | Sequence of bytes | bytearray(b'Some ASCII')bytearray(b"Some ASCII")bytearray([119, 105, 107, 105])
|
bytes
|
immutable | Sequence of bytes | b'Some ASCII'b"Some ASCII"bytes([119, 105, 107, 105])
|
complex
|
immutable | Complex number with real and imaginary parts | 3+2.7j3 + 2.7j
|
dict
|
mutable | Associative array (or dictionary) of key and value pairs; can contain mixed types (keys and values), keys must be a hashable type | {'key1': 1.0, 3: False}{}
|
types.EllipsisType
|
immutable | An ellipsis placeholder to be used as an index in NumPy arrays | ...Ellipsis
|
float
|
immutable | Double-precision floating-point number. The precision is machine-dependent but in practice is generally implemented as a 64-bit IEEE 754 number with 53 bits of precision.[120] |
|
frozenset
|
immutable | Unordered set, contains no duplicates; can contain mixed types, if hashable | frozenset([4.0, 'string', True])
|
int
|
immutable | Integer of unlimited magnitude[121] | 42
|
list
|
mutable | List, can contain mixed types | [4.0, 'string', True][]
|
types.NoneType
|
immutable | An object representing the absence of a value, often called null in other languages | None
|
types.NotImplementedType
|
immutable | A placeholder that can be returned from overloaded operators to indicate unsupported operand types. | NotImplemented
|
range
|
immutable | An immutable sequence of numbers commonly used for looping a specific number of times in for loops[122]
|
range(−1, 10)range(10, −5, −2)
|
set
|
mutable | Unordered set, contains no duplicates; can contain mixed types, if hashable | {4.0, 'string', True}set()
|
str
|
immutable | A character string: sequence of Unicode codepoints | 'Wikipedia'"Wikipedia""""Spanning
multiple
lines"""
Spanning
multiple
lines
|
tuple
|
immutable | Can contain mixed types | (4.0, 'string', True)('single element',)()
|
Arithmetic operations
[edit]Python has the usual symbols for arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /), the floor division operator // and the modulo operation % (where the remainder can be negative, e.g. 4 % -3 == -2). It also has ** for exponentiation, e.g. 5**3 == 125 and 9**0.5 == 3.0, and a matrix‑multiplication operator @ .[123] These operators work like in traditional math; with the same precedence rules, the operators infix (+ and - can also be unary to represent positive and negative numbers respectively).
The division between integers produces floating-point results. The behavior of division has changed significantly over time:[124]
- Current Python (i.e. since 3.0) changed
/to always be floating-point division, e.g.5/2 == 2.5. - The floor division
//operator was introduced. So7//3 == 2,-7//3 == -3,7.5//3 == 2.0and-7.5//3 == -3.0. Addingfrom __future__ import divisioncauses a module used in Python 2.7 to use Python 3.0 rules for division (see above).
In Python terms, / is true division (or simply division), and // is floor division. / before version 3.0 is classic division.[124]
Rounding towards negative infinity, though different from most languages, adds consistency. For instance, it means that the equation (a + b)//b == a//b + 1 is always true. It also means that the equation b*(a//b) + a%b == a is valid for both positive and negative values of a. However, maintaining the validity of this equation means that while the result of a%b is, as expected, in the half-open interval [0, b), where b is a positive integer, it has to lie in the interval (b, 0] when b is negative.[125]
Python provides a round function for rounding a float to the nearest integer. For tie-breaking, Python 3 uses round to even: round(1.5) and round(2.5) both produce 2.[126] Versions before 3 used round-away-from-zero: round(0.5) is 1.0, round(-0.5) is −1.0.[127]
Python allows Boolean expressions with multiple equality relations in a manner that is consistent with general use in mathematics. For example, the expression a < b < c tests whether a is less than b and b is less than c.[128] C-derived languages interpret this expression differently: in C, the expression would first evaluate a < b, resulting in 0 or 1, and that result would then be compared with c.[129]
Python uses arbitrary-precision arithmetic for all integer operations. The Decimal type/class in the decimal module provides decimal floating-point numbers to a pre-defined arbitrary precision and several rounding modes.[130] The Fraction class in the fractions module provides arbitrary precision for rational numbers.[131]
Due to Python's extensive mathematics library, and the third-party library NumPy that further extends the native capabilities, it is frequently used as a scientific scripting language to aid in problems such as numerical data processing and manipulation.[132][133]
Programming examples
[edit]print('Hello, world!')
Program to calculate the factorial of a positive integer:
n = int(input('Type a number, and its factorial will be printed: '))
if n < 0:
raise ValueError('You must enter a non-negative integer')
factorial = 1
for i in range(2, n + 1):
factorial *= i
print(factorial)
Libraries
[edit]Python's large standard library[134] provides tools suited to many tasks and is commonly cited as one of its greatest strengths. For Internet-facing applications, many standard formats and protocols such as MIME and HTTP are supported. It includes modules for creating graphical user interfaces, connecting to relational databases, generating pseudorandom numbers, arithmetic with arbitrary-precision decimals,[130] manipulating regular expressions, and unit testing.
Some parts of the standard library are covered by specifications—for example, the Web Server Gateway Interface (WSGI) implementation wsgiref follows PEP 333[135]—but most are specified by their code, internal documentation, and test suites. However, because most of the standard library is cross-platform Python code, only a few modules need altering or rewriting for variant implementations.
As of 17 March 2024,[update] the Python Package Index (PyPI), the official repository for third-party Python software, contains over 523,000[136] packages with a wide range of functionality, including:
Development environments
[edit]Most Python implementations (including CPython) include a read–eval–print loop (REPL), permitting them to function as a command line interpreter for which users enter statements sequentially and receive results immediately.
Python also comes with an Integrated development environment (IDE) called IDLE, which is more beginner-oriented.
Other shells, including IDLE and IPython, add further abilities such as improved auto-completion, session state retention, and syntax highlighting.
As well as standard desktop integrated development environments including PyCharm, IntelliJ Idea, Visual Studio Code etc, there are web browser-based IDEs, including SageMath, for developing science- and math-related programs; PythonAnywhere, a browser-based IDE and hosting environment; and Canopy IDE, a commercial IDE emphasizing scientific computing.[137]
Implementations
[edit]Reference implementation
[edit]CPython is the reference implementation of Python. It is written in C, meeting the C89 standard (Python 3.11 uses C11[138]) with several select C99 features. CPython includes its own C extensions, but third-party extensions are not limited to older C versions—e.g. they can be implemented with C11 or C++.[139][140] CPython compiles Python programs into an intermediate bytecode[141] which is then executed by its virtual machine.[142] CPython is distributed with a large standard library written in a mixture of C and native Python, and is available for many platforms, including Windows (starting with Python 3.9, the Python installer deliberately fails to install on Windows 7 and 8;[143][144] Windows XP was supported until Python 3.5) and most modern Unix-like systems, including macOS (and Apple M1 Macs, since Python 3.9.1, with experimental installer), with unofficial support for VMS.[145] Platform portability was one of its earliest priorities.[146] (During Python 1 and 2 development, even OS/2 and Solaris were supported,[147] but support has since been dropped for many platforms.)
All current Python versions (i.e. since 3.7) only support operating systems with multi-threading support.
Other implementations
[edit]All alternative implementations have at least slightly different semantics (e.g. may have unordered dictionaries, unlike all current Python versions), e.g. with the larger Python ecosystem, such as with supporting the C Python API of with PyPy:
- PyPy is a fast, compliant interpreter of Python 2.7 and 3.10.[148][149] Its just-in-time compiler often brings a significant speed improvement over CPython, but some libraries written in C cannot be used with it.[150] It has e.g. RISC-V support.
- Codon is a language with an ahead-of-time (AOT) compiler, that (AOT) compiles a statically-typed Python-like language with "syntax and semantics are nearly identical to Python's, there are some notable differences"[151] e.g. it uses 64-bit machine integers, for speed, not arbitrary like Python, and it claims speedups over CPython are usually on the order of 10–100x. It compiles to machine code (via LLVM) and supports native multithreading.[152] Codon can also compile to Python extension modules that can be imported and used from Python.
- Stackless Python is a significant fork of CPython that implements microthreads; it does not use the call stack in the same way, thus allowing massively concurrent programs. PyPy also has a stackless version.[153]
- MicroPython and CircuitPython are Python 3 variants optimized for microcontrollers, including Lego Mindstorms EV3.[154]
- Pyston is a variant of the Python runtime that uses just-in-time compilation to speed up the execution of Python programs.[155]
- Cinder is a performance-oriented fork of CPython 3.8 that contains a number of optimizations, including bytecode inline caching, eager evaluation of coroutines, a method-at-a-time JIT, and an experimental bytecode compiler.[156]
- Snek[157][158][159] Embedded Computing Language (compatible with e.g. 8-bit AVR microcontrollers such as ATmega 328P-based Arduino, as well as larger ones compatible with MicroPython) "is Python-inspired, but it is not Python. It is possible to write Snek programs that run under a full Python system, but most Python programs will not run under Snek."[160] It is an imperative language not including OOP / classes, unlike Python, and simplifying to one number type with 32-bit single-precision (similar to JavaScript, except smaller).
No longer supported implementations
[edit]Other just-in-time Python compilers have been developed, but are now unsupported:
- Google began a project named Unladen Swallow in 2009, with the aim of speeding up the Python interpreter five-fold by using the LLVM, and of improving its multithreading ability to scale to thousands of cores,[161] while ordinary implementations suffer from the global interpreter lock.
- Psyco is a discontinued just-in-time specializing compiler that integrates with CPython and transforms bytecode to machine code at runtime. The emitted code is specialized for certain data types and is faster than the standard Python code. Psyco does not support Python 2.7 or later.
- PyS60 was a Python 2 interpreter for Series 60 mobile phones released by Nokia in 2005. It implemented many of the modules from the standard library and some additional modules for integrating with the Symbian operating system. The Nokia N900 also supports Python with GTK widget libraries, enabling programs to be written and run on the target device.[162]
Cross-compilers to other languages
[edit]There are several compilers/transpilers to high-level object languages, with either unrestricted Python, a restricted subset of Python, or a language similar to Python as the source language:
- Brython,[163] Transcrypt[164][165] and Pyjs (latest release in 2012) compile Python to JavaScript.
- Cython compiles (a superset of) Python to C. The resulting code is also usable with Python via direct C-level API calls into the Python interpreter.
- PyJL compiles/transpiles a subset of Python to "human-readable, maintainable, and high-performance Julia source code".[90] Despite claiming high performance, no tool can claim to do that for arbitrary Python code; i.e. it's known not possible to compile to a faster language or machine code. Unless semantics of Python are changed, but in many cases speedup is possible with few or no changes in the Python code. The faster Julia source code can then be used from Python, or compiled to machine code, and based that way.
- Nuitka compiles Python into C.[166] It works with Python 3.4 to 3.12 (and 2.6 and 2.7), for Python's main supported platforms (and Windows 7 or even Windows XP) and for Android. It claims complete support for Python 3.10, some support for 3.11 and 3.12 and experimental support for Python 3.13. It supports macOS including Apple Silicon-based. It's a free compiler, though it also has commercial add-ons (e.g. for hiding source code).
- Numba is used from Python, as a tool (enabled by adding a decorator to relevant Python code), a JIT compiler that translates a subset of Python and NumPy code into fast machine code.
- Pythran compiles a subset of Python 3 to C++ (C++11).[167]
- RPython can be compiled to C, and is used to build the PyPy interpreter of Python.
- The Python → 11l → C++ transpiler[168] compiles a subset of Python 3 to C++ (C++17).
Specialized:
- MyHDL is a Python-based hardware description language (HDL), that converts MyHDL code to Verilog or VHDL code.
Older projects (or not to be used with Python 3.x and latest syntax):
- Google's Grumpy (latest release in 2017) transpiles Python 2 to Go.[169][170][171]
- IronPython allows running Python 2.7 programs (and an alpha, released in 2021, is also available for "Python 3.4, although features and behaviors from later versions may be included"[172]) on the .NET Common Language Runtime.[173]
- Jython compiles Python 2.7 to Java bytecode, allowing the use of the Java libraries from a Python program.[174]
- Pyrex (latest release in 2010) and Shed Skin (latest release in 2013) compile to C and C++ respectively.
Performance
[edit]Performance comparison of various Python implementations on a non-numerical (combinatorial) workload was presented at EuroSciPy '13.[175] Python's performance compared to other programming languages is also benchmarked by The Computer Language Benchmarks Game.[176]
Development
[edit]Python's development is conducted largely through the Python Enhancement Proposal (PEP) process, the primary mechanism for proposing major new features, collecting community input on issues, and documenting Python design decisions.[177] Python coding style is covered in PEP 8.[178] Outstanding PEPs are reviewed and commented on by the Python community and the steering council.[177]
Enhancement of the language corresponds with the development of the CPython reference implementation. The mailing list python-dev is the primary forum for the language's development. Specific issues were originally discussed in the Roundup bug tracker hosted at by the foundation.[179] In 2022, all issues and discussions were migrated to GitHub.[180] Development originally took place on a self-hosted source-code repository running Mercurial, until Python moved to GitHub in January 2017.[181]
CPython's public releases come in three types, distinguished by which part of the version number is incremented:
- Backward-incompatible versions, where code is expected to break and needs to be manually ported. The first part of the version number is incremented. These releases happen infrequently—version 3.0 was released 8 years after 2.0. According to Guido van Rossum, a version 4.0 is very unlikely to ever happen.[182]
- Major or "feature" releases are largely compatible with the previous version but introduce new features. The second part of the version number is incremented. Starting with Python 3.9, these releases are expected to happen annually.[183][184] Each major version is supported by bug fixes for several years after its release.[185]
- Bugfix releases,[186] which introduce no new features, occur about every 3 months and are made when a sufficient number of bugs have been fixed upstream since the last release. Security vulnerabilities are also patched in these releases. The third and final part of the version number is incremented.[186]
Many alpha, beta, and release-candidates are also released as previews and for testing before final releases. Although there is a rough schedule for each release, they are often delayed if the code is not ready. Python's development team monitors the state of the code by running the large unit test suite during development.[187]
The major academic conference on Python is PyCon. There are also special Python mentoring programs, such as PyLadies.
Python 3.12 removed wstr meaning Python extensions[188] need to be modified,[189] and 3.10 added pattern matching to the language.[190]
Python 3.12 dropped some outdated modules, and more will be dropped in the future, deprecated as of 3.13; already deprecated array 'u' format code will emit DeprecationWarning since 3.13 and will be removed in Python 3.16. The 'w' format code should be used instead. Part of ctypes is also deprecated and http.server.CGIHTTPRequestHandler will emit a DeprecationWarning, and will be removed in 3.15. Using that code already has a high potential for both security and functionality bugs. Parts of the typing module are deprecated, e.g. creating a typing.NamedTuple class using keyword arguments to denote the fields and such (and more) will be disallowed in Python 3.15.
API documentation generators
[edit]Tools that can generate documentation for Python API include pydoc (available as part of the standard library), Sphinx, Pdoc and its forks, Doxygen and Graphviz, among others.[191]
Naming
[edit]Python's name is derived from the British comedy group Monty Python, whom Python creator Guido van Rossum enjoyed while developing the language. Monty Python references appear frequently in Python code and culture;[192] for example, the metasyntactic variables often used in Python literature are spam and eggs instead of the traditional foo and bar.[192][193] The official Python documentation also contains various references to Monty Python routines.[194][195] Users of Python are sometimes referred to as "Pythonistas".[196]
The prefix Py- is used to show that something is related to Python. Examples of the use of this prefix in names of Python applications or libraries include Pygame, a binding of Simple DirectMedia Layer to Python (commonly used to create games); PyQt and PyGTK, which bind Qt and GTK to Python respectively; and PyPy, a Python implementation originally written in Python.
Popularity
[edit]Since 2003, Python has consistently ranked in the top ten most popular programming languages in the TIOBE Programming Community Index where as of December 2022[update] it was the most popular language (ahead of C, C++, and Java).[39] It was selected as Programming Language of the Year (for "the highest rise in ratings in a year") in 2007, 2010, 2018, and 2020 (the only language to have done so four times as of 2020[update][197]).
Large organizations that use Python include Wikipedia, Google,[198] Yahoo!,[199] CERN,[200] NASA,[201] Facebook,[202] Amazon, Instagram,[203] Spotify,[204] and some smaller entities like Industrial Light & Magic[205] and ITA.[206] The social news networking site Reddit was written mostly in Python.[207] Organizations that partially use Python include Discord[208] and Baidu.[209]
Uses
[edit]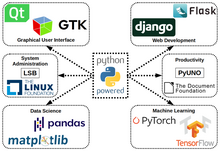
Python can serve as a scripting language for web applications, e.g. via mod_wsgi for the Apache webserver.[210] With Web Server Gateway Interface, a standard API has evolved to facilitate these applications. Web frameworks like Django, Pylons, Pyramid, TurboGears, web2py, Tornado, Flask, Bottle, and Zope support developers in the design and maintenance of complex applications. Pyjs and IronPython can be used to develop the client-side of Ajax-based applications. SQLAlchemy can be used as a data mapper to a relational database. Twisted is a framework to program communications between computers, and is used (for example) by Dropbox.
Libraries such as NumPy, SciPy and Matplotlib allow the effective use of Python in scientific computing,[211][212] with specialized libraries such as Biopython and Astropy providing domain-specific functionality. SageMath is a computer algebra system with a notebook interface programmable in Python: its library covers many aspects of mathematics, including algebra, combinatorics, numerical mathematics, number theory, and calculus.[213] OpenCV has Python bindings with a rich set of features for computer vision and image processing.[214]
Python is commonly used in artificial intelligence projects and machine learning projects with the help of libraries like TensorFlow, Keras, Pytorch, scikit-learn and the Logic language ProbLog.[215][216][217][218][219] As a scripting language with a modular architecture, simple syntax, and rich text processing tools, Python is often used for natural language processing.[220]
The combination of Python and Prolog has proved to be particularly useful for AI applications, with Prolog providing knowledge representation and reasoning capabilities. The Janus system, in particular, exploits the similarities between these two languages, in part because of their use of dynamic typing, and the simple recursive nature of their data structures. Typical applications of this combination include natural language processing, visual query answering, geospatial reasoning, and handling of semantic web data.[221][222] The Natlog system, implemented in Python, uses Definite Clause Grammars (DCGs) as prompt generators for text-to-text generators like GPT3 and text-to-image generators like DALL-E or Stable Diffusion.[223]
Python can also be used for graphical user interface (GUI) by using libraries like Tkinter.[224][225]
Python has been successfully embedded in many software products as a scripting language, including in finite element method software such as Abaqus, 3D parametric modelers like FreeCAD, 3D animation packages such as 3ds Max, Blender, Cinema 4D, Lightwave, Houdini, Maya, modo, MotionBuilder, Softimage, the visual effects compositor Nuke, 2D imaging programs like GIMP,[226] Inkscape, Scribus and Paint Shop Pro,[227] and musical notation programs like scorewriter and capella. GNU Debugger uses Python as a pretty printer to show complex structures such as C++ containers. Esri promotes Python as the best choice for writing scripts in ArcGIS.[228] It has also been used in several video games,[229][230] and has been adopted as first of the three available programming languages in Google App Engine, the other two being Java and Go.[231]
Many operating systems include Python as a standard component. It ships with most Linux distributions,[232] AmigaOS 4 (using Python 2.7), FreeBSD (as a package), NetBSD, and OpenBSD (as a package) and can be used from the command line (terminal). Many Linux distributions use installers written in Python: Ubuntu uses the Ubiquity installer, while Red Hat Linux and Fedora Linux use the Anaconda installer. Gentoo Linux uses Python in its package management system, Portage.
Python is used extensively in the information security industry, including in exploit development.[233][234]
Most of the Sugar software for the One Laptop per Child XO, developed at Sugar Labs as of 2008[update], is written in Python.[235] The Raspberry Pi single-board computer project has adopted Python as its main user-programming language.
LibreOffice includes Python and intends to replace Java with Python. Its Python Scripting Provider is a core feature[236] since Version 4.0 from 7 February 2013.
Languages influenced by Python
[edit]Python's design and philosophy have influenced many other programming languages:
- Boo uses indentation, a similar syntax, and a similar object model.[237]
- Cobra uses indentation and a similar syntax, and its Acknowledgements document lists Python first among languages that influenced it.[238]
- CoffeeScript, a programming language that cross-compiles to JavaScript, has Python-inspired syntax.
- ECMAScript–JavaScript borrowed iterators and generators from Python.[239]
- GDScript, a scripting language very similar to Python, built-in to the Godot game engine.[240]
- Go is designed for the "speed of working in a dynamic language like Python"[241] and shares the same syntax for slicing arrays.
- Groovy was motivated by the desire to bring the Python design philosophy to Java.[242]
- Julia was designed to be "as usable for general programming as Python".[27]
- Mojo is a non-strict[28][243] superset of Python (e.g. still missing classes, and adding e.g. struct).[244]
- Nim uses indentation and similar syntax.[245]
- Ruby's creator, Yukihiro Matsumoto, has said: "I wanted a scripting language that was more powerful than Perl, and more object-oriented than Python. That's why I decided to design my own language."[246]
- Swift, a programming language developed by Apple, has some Python-inspired syntax.[247]
- Kotlin blends Python and Java features, minimizing boilerplate code for enhanced developer efficiency.[248]
Python's development practices have also been emulated by other languages. For example, the practice of requiring a document describing the rationale for, and issues surrounding, a change to the language (in Python, a PEP) is also used in Tcl,[249] Erlang,[250] and Swift.[251]
See also
[edit]- Python syntax and semantics
- pip (package manager)
- List of programming languages
- History of programming languages
- Comparison of programming languages
References
[edit]- ^ "General Python FAQ – Python 3 documentation". docs.python.org. Retrieved 7 July 2024.
- ^ "Python 0.9.1 part 01/21". alt.sources archives. Archived from the original on 11 August 2021. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ^ "Why is Python a dynamic language and also a strongly typed language". Python Wiki. Archived from the original on 14 March 2021. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- ^ a b "PEP 483 – The Theory of Type Hints". Python.org. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "PEP 11 – CPython platform support | peps.python.org". Python Enhancement Proposals (PEPs). Retrieved 22 April 2024.
- ^ "PEP 738 – Adding Android as a supported platform | peps.python.org". Python Enhancement Proposals (PEPs). Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- ^ "Download Python for Other Platforms". Python.org. Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ "test – Regression tests package for Python – Python 3.7.13 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 17 May 2022.
- ^ "platform – Access to underlying platform's identifying data – Python 3.10.4 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 17 May 2022.
- ^ Holth, Moore (30 March 2014). "PEP 0441 – Improving Python ZIP Application Support". Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 12 November 2015.
- ^ "Starlark Language". Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- ^ a b "Why was Python created in the first place?". General Python FAQ. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 22 March 2007.
I had extensive experience with implementing an interpreted language in the ABC group at CWI, and from working with this group I had learned a lot about language design. This is the origin of many Python features, including the use of indentation for statement grouping and the inclusion of very high-level data types (although the details are all different in Python).
- ^ "Ada 83 Reference Manual (raise statement)". Archived from the original on 22 October 2019. Retrieved 7 January 2020.
- ^ a b Kuchling, Andrew M. (22 December 2006). "Interview with Guido van Rossum (July 1998)". amk.ca. Archived from the original on 1 May 2007. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
I'd spent a summer at DEC's Systems Research Center, which introduced me to Modula-2+; the Modula-3 final report was being written there at about the same time. What I learned there later showed up in Python's exception handling, modules, and the fact that methods explicitly contain 'self' in their parameter list. String slicing came from Algol-68 and Icon.
- ^ a b c "itertools – Functions creating iterators for efficient looping – Python 3.7.1 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
This module implements a number of iterator building blocks inspired by constructs from APL, Haskell, and SML.
- ^ van Rossum, Guido (1993). "An Introduction to Python for UNIX/C Programmers". Proceedings of the NLUUG Najaarsconferentie (Dutch UNIX Users Group). CiteSeerX 10.1.1.38.2023.
even though the design of C is far from ideal, its influence on Python is considerable.
- ^ a b "Classes". The Python Tutorial. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 23 October 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
It is a mixture of the class mechanisms found in C++ and Modula-3
- ^ Lundh, Fredrik. "Call By Object". effbot.org. Archived from the original on 23 November 2019. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
replace "CLU" with "Python", "record" with "instance", and "procedure" with "function or method", and you get a pretty accurate description of Python's object model.
- ^ Simionato, Michele. "The Python 2.3 Method Resolution Order". Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 20 August 2020. Retrieved 29 July 2014.
The C3 method itself has nothing to do with Python, since it was invented by people working on Dylan and it is described in a paper intended for lispers
- ^ Kuchling, A. M. "Functional Programming HOWTO". Python v2.7.2 documentation. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 9 February 2012.
List comprehensions and generator expressions [...] are a concise notation for such operations, borrowed from the functional programming language Haskell.
- ^ Schemenauer, Neil; Peters, Tim; Hetland, Magnus Lie (18 May 2001). "PEP 255 – Simple Generators". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 9 February 2012.
- ^ "More Control Flow Tools". Python 3 documentation. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2016. Retrieved 24 July 2015.
By popular demand, a few features commonly found in functional programming languages like Lisp have been added to Python. With the lambda keyword, small anonymous functions can be created.
- ^ "re – Regular expression operations – Python 3.10.6 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 18 July 2018. Retrieved 6 September 2022.
This module provides regular expression matching operations similar to those found in Perl.
- ^ "CoffeeScript". coffeescript.org. Archived from the original on 12 June 2020. Retrieved 3 July 2018.
- ^ "Perl and Python influences in JavaScript". www.2ality.com. 24 February 2013. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- ^ Rauschmayer, Axel. "Chapter 3: The Nature of JavaScript; Influences". O'Reilly, Speaking JavaScript. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- ^ a b "Why We Created Julia". Julia website. February 2012. Archived from the original on 2 May 2020. Retrieved 5 June 2014.
We want something as usable for general programming as Python [...]
- ^ a b Krill, Paul (4 May 2023). "Mojo language marries Python and MLIR for AI development". InfoWorld. Archived from the original on 5 May 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ Ring Team (4 December 2017). "Ring and other languages". ring-lang.net. ring-lang. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ Bini, Ola (2007). Practical JRuby on Rails Web 2.0 Projects: bringing Ruby on Rails to the Java platform. Berkeley: APress. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-59059-881-8.
- ^ Lattner, Chris (3 June 2014). "Chris Lattner's Homepage". Chris Lattner. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 3 June 2014.
The Swift language is the product of tireless effort from a team of language experts, documentation gurus, compiler optimization ninjas, and an incredibly important internal dogfooding group who provided feedback to help refine and battle-test ideas. Of course, it also greatly benefited from the experiences hard-won by many other languages in the field, drawing ideas from Objective-C, Rust, Haskell, Ruby, Python, C#, CLU, and far too many others to list.
- ^ Kuhlman, Dave. "A Python Book: Beginning Python, Advanced Python, and Python Exercises". Section 1.1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 June 2012.
- ^ "About Python". Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 20 April 2012. Retrieved 24 April 2012., second section "Fans of Python use the phrase "batteries included" to describe the standard library, which covers everything from asynchronous processing to zip files."
- ^ "PEP 206 – Python Advanced Library". Python.org. Archived from the original on 5 May 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ Rossum, Guido Van (20 January 2009). "The History of Python: A Brief Timeline of Python". The History of Python. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- ^ Peterson, Benjamin (20 April 2020). "Python 2.7.18, the last release of Python 2". Python Insider. Archived from the original on 26 April 2020. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- ^ "Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2022". Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on 27 June 2022. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
- ^ "The State of Developer Ecosystem in 2020 Infographic". JetBrains: Developer Tools for Professionals and Teams. Archived from the original on 1 March 2021. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- ^ a b "TIOBE Index". TIOBE. Archived from the original on 25 February 2018. Retrieved 3 January 2023.
The TIOBE Programming Community index is an indicator of the popularity of programming languages
Updated as required. - ^ "PYPL PopularitY of Programming Language index". pypl.github.io. Archived from the original on 14 March 2017. Retrieved 26 March 2021.
- ^ a b Venners, Bill (13 January 2003). "The Making of Python". Artima Developer. Artima. Archived from the original on 1 September 2016. Retrieved 22 March 2007.
- ^ van Rossum, Guido (29 August 2000). "SETL (was: Lukewarm about range literals)". Python-Dev (Mailing list). Archived from the original on 14 July 2018. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ van Rossum, Guido (20 January 2009). "A Brief Timeline of Python". The History of Python. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 20 January 2009.
- ^ Fairchild, Carlie (12 July 2018). "Guido van Rossum Stepping Down from Role as Python's Benevolent Dictator For Life". Linux Journal. Archived from the original on 13 July 2018. Retrieved 13 July 2018.
- ^ "PEP 8100". Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2019.
- ^ "PEP 13 – Python Language Governance". Python.org. Archived from the original on 27 May 2021. Retrieved 25 August 2021.
- ^ Kuchling, A. M.; Zadka, Moshe (16 October 2000). "What's New in Python 2.0". Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 23 October 2012. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ^ van Rossum, Guido (5 April 2006). "PEP 3000 – Python 3000". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 27 June 2009.
- ^ "2to3 – Automated Python 2 to 3 code translation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 2 February 2021.
- ^ "PEP 373 – Python 2.7 Release Schedule". python.org. Archived from the original on 19 May 2020. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ^ "PEP 466 – Network Security Enhancements for Python 2.7.x". python.org. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ^ "Sunsetting Python 2". Python.org. Archived from the original on 12 January 2020. Retrieved 22 September 2019.
- ^ "PEP 373 – Python 2.7 Release Schedule". Python.org. Archived from the original on 13 January 2020. Retrieved 22 September 2019.
- ^ "Python Release Python 3.7.17". Python.org. Archived from the original on 31 July 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ mattip (25 December 2023). "PyPy v7.3.14 release". PyPy. Archived from the original on 5 January 2024. Retrieved 5 January 2024.
- ^ "CVE-2021-3177". Red Hat Customer Portal. Archived from the original on 6 March 2021. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ^ "CVE-2021-3177". CVE. Archived from the original on 27 February 2021. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ^ "CVE-2021-23336". CVE. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ^ Langa, Łukasz (24 March 2022). "Python 3.10.4 and 3.9.12 are now available out of schedule". Python Insider. Archived from the original on 21 April 2022. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Langa, Łukasz (16 March 2022). "Python 3.10.3, 3.9.11, 3.8.13, and 3.7.13 are now available with security content". Python Insider. Archived from the original on 17 April 2022. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ Langa, Łukasz (17 May 2022). "Python 3.9.13 is now available". Python Insider. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 21 May 2022.
- ^ Langa, Łukasz (7 September 2022). "Python releases 3.10.7, 3.9.14, 3.8.14, and 3.7.14 are now available". Python Insider. Archived from the original on 13 September 2022. Retrieved 16 September 2022.
- ^ "CVE-2020-10735". CVE. Archived from the original on 20 September 2022. Retrieved 16 September 2022.
- ^ "Built-in Types".
- ^ corbet (24 October 2022). "Python 3.11 released [LWN.net]". lwn.net. Retrieved 15 November 2022.
- ^ "What's New In Python 3.13". Python documentation. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ^ "PEP 667 – Consistent views of namespaces | peps.python.org". Python Enhancement Proposals (PEPs). Retrieved 7 October 2024.
- ^ "Status of Python versions". Python Developer's Guide. Retrieved 7 October 2024.
- ^ Wouters, Thomas (9 April 2024). "Python Insider: Python 3.12.3 and 3.13.0a6 released". Python Insider. Retrieved 29 April 2024.
- ^ "PEP 594 – Removing dead batteries from the standard library". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Softtware Foundation. 20 May 2019.
- ^ Hugo (15 October 2024). "Python Insider: Python 3.14.0 alpha 1 is now available". Python Insider. Retrieved 16 October 2024.
- ^ "PEP 649 – Deferred Evaluation Of Annotations Using Descriptors | peps.python.org". Python Enhancement Proposals (PEPs). Retrieved 16 October 2024.
- ^ The Cain Gang Ltd. "Python Metaclasses: Who? Why? When?" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 May 2009. Retrieved 27 June 2009.
- ^ "3.3. Special method names". The Python Language Reference. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 27 June 2009.
- ^ "PyDBC: method preconditions, method postconditions and class invariants for Python". Archived from the original on 23 November 2019. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ "Contracts for Python". Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ "PyDatalog". Archived from the original on 13 June 2020. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "Glue It All Together With Python". Python.org. Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- ^ "Extending and Embedding the Python Interpreter: Reference Counts". Docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 18 October 2012. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
Since Python makes heavy use of
malloc()andfree(), it needs a strategy to avoid memory leaks as well as the use of freed memory. The chosen method is called reference counting. - ^ a b Hettinger, Raymond (30 January 2002). "PEP 289 – Generator Expressions". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ^ "6.5 itertools – Functions creating iterators for efficient looping". Docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
- ^ a b Peters, Tim (19 August 2004). "PEP 20 – The Zen of Python". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ Lutz, Mark (January 2022). "Python Changes 2014+". Learning Python. Archived from the original on 15 March 2024. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ "Confusion regarding a rule in The Zen of Python". Python Help - Discussions on Python.org. 3 May 2022. Archived from the original on 25 February 2024. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ Ambi, Chetan (4 July 2021). "The Most Controversial Python Walrus Operator". Python Simplified. Archived from the original on 27 August 2023. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ Grifski, Jeremy (24 May 2020). "The Controversy Behind The Walrus Operator in Python". The Renegade Coder. Archived from the original on 28 December 2023. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ Bader, Dan. "Python String Formatting Best Practices". Real Python. Archived from the original on 18 February 2024. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ Martelli, Alex; Ravenscroft, Anna; Ascher, David (2005). Python Cookbook, 2nd Edition. O'Reilly Media. p. 230. ISBN 978-0-596-00797-3. Archived from the original on 23 February 2020. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- ^ "Python Culture". ebeab. 21 January 2014. Archived from the original on 30 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Transpiling Python to Julia using PyJL" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 November 2023. Retrieved 20 September 2023.
After manually modifying one line of code by specifying the necessary type information, we obtained a speedup of 52.6×, making the translated Julia code 19.5× faster than the original Python code.
- ^ "Why is it called Python?". General Python FAQ. Docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 3 January 2023.
- ^ "15 Ways Python Is a Powerful Force on the Web". Archived from the original on 11 May 2019. Retrieved 3 July 2018.
- ^ "pprint – Data pretty printer – Python 3.11.0 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2022.
stuff=['spam', 'eggs', 'lumberjack', 'knights', 'ni']
- ^ "Code Style – The Hitchhiker's Guide to Python". docs.python-guide.org. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ "Is Python a good language for beginning programmers?". General Python FAQ. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 21 March 2007.
- ^ "Myths about indentation in Python". Secnetix.de. Archived from the original on 18 February 2018. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ Guttag, John V. (12 August 2016). Introduction to Computation and Programming Using Python: With Application to Understanding Data. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-52962-4.
- ^ "PEP 8 – Style Guide for Python Code". Python.org. Archived from the original on 17 April 2019. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- ^ "8. Errors and Exceptions – Python 3.12.0a0 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 9 May 2022. Retrieved 9 May 2022.
- ^ "Highlights: Python 2.5". Python.org. Archived from the original on 4 August 2019. Retrieved 20 March 2018.
- ^ van Rossum, Guido (22 April 2009). "Tail Recursion Elimination". Neopythonic.blogspot.be. Archived from the original on 19 May 2018. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ^ van Rossum, Guido (9 February 2006). "Language Design Is Not Just Solving Puzzles". Artima forums. Artima. Archived from the original on 17 January 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2007.
- ^ van Rossum, Guido; Eby, Phillip J. (10 May 2005). "PEP 342 – Coroutines via Enhanced Generators". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 29 May 2020. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ^ "PEP 380". Python.org. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ^ "division". python.org. Archived from the original on 20 July 2006. Retrieved 30 July 2014.
- ^ "PEP 0465 – A dedicated infix operator for matrix multiplication". python.org. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- ^ "Python 3.5.1 Release and Changelog". python.org. Archived from the original on 14 May 2020. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- ^ "What's New in Python 3.8". Archived from the original on 8 June 2020. Retrieved 14 October 2019.
- ^ van Rossum, Guido; Hettinger, Raymond (7 February 2003). "PEP 308 – Conditional Expressions". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 13 March 2016. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ^ "4. Built-in Types – Python 3.6.3rc1 documentation". python.org. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- ^ "5.3. Tuples and Sequences – Python 3.7.1rc2 documentation". python.org. Archived from the original on 10 June 2020. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- ^ a b "PEP 498 – Literal String Interpolation". python.org. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- ^ "Why must 'self' be used explicitly in method definitions and calls?". Design and History FAQ. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ^ Sweigart, Al (2020). Beyond the Basic Stuff with Python: Best Practices for Writing Clean Code. No Starch Press. p. 322. ISBN 978-1-59327-966-0. Archived from the original on 13 August 2021. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ "The Python Language Reference, section 3.3. New-style and classic classes, for release 2.7.1". Archived from the original on 26 October 2012. Retrieved 12 January 2011.
- ^ "PEP 484 – Type Hints | peps.python.org". peps.python.org. Archived from the original on 27 November 2023. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ "typing — Support for type hints". Python documentation. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 21 February 2020. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
- ^ "mypy – Optional Static Typing for Python". Archived from the original on 6 June 2020. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ^ "Introduction". mypyc.readthedocs.io. Archived from the original on 22 December 2023. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
- ^ "15. Floating Point Arithmetic: Issues and Limitations – Python 3.8.3 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 6 June 2020. Retrieved 6 June 2020.
Almost all machines today (November 2000) use IEEE-754 floating point arithmetic, and almost all platforms map Python floats to IEEE-754 "double precision".
- ^ Zadka, Moshe; van Rossum, Guido (11 March 2001). "PEP 237 – Unifying Long Integers and Integers". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 28 May 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ "Built-in Types". Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
- ^ "PEP 465 – A dedicated infix operator for matrix multiplication". python.org. Archived from the original on 29 May 2020. Retrieved 3 July 2018.
- ^ a b Zadka, Moshe; van Rossum, Guido (11 March 2001). "PEP 238 – Changing the Division Operator". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 28 May 2020. Retrieved 23 October 2013.
- ^ "Why Python's Integer Division Floors". 24 August 2010. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- ^ "round", The Python standard library, release 3.2, §2: Built-in functions, archived from the original on 25 October 2012, retrieved 14 August 2011
- ^ "round", The Python standard library, release 2.7, §2: Built-in functions, archived from the original on 27 October 2012, retrieved 14 August 2011
- ^ Beazley, David M. (2009). Python Essential Reference (4th ed.). Addison-Wesley Professional. p. 66. ISBN 9780672329784.
- ^ Kernighan, Brian W.; Ritchie, Dennis M. (1988). The C Programming Language (2nd ed.). p. 206.
- ^ a b Batista, Facundo (17 October 2003). "PEP 327 – Decimal Data Type". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ "What's New in Python 2.6". Python v2.6.9 documentation. 29 October 2013. Archived from the original on 23 December 2019. Retrieved 26 September 2015.
- ^ "10 Reasons Python Rocks for Research (And a Few Reasons it Doesn't) – Hoyt Koepke". University of Washington Department of Statistics. Archived from the original on 31 May 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2019.
- ^ Shell, Scott (17 June 2014). "An introduction to Python for scientific computing" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 February 2019. Retrieved 3 February 2019.
- ^ Piotrowski, Przemyslaw (July 2006). "Build a Rapid Web Development Environment for Python Server Pages and Oracle". Oracle Technology Network. Oracle. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
- ^ Eby, Phillip J. (7 December 2003). "PEP 333 – Python Web Server Gateway Interface v1.0". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ^ "PyPI". PyPI. 17 March 2024. Archived from the original on 17 March 2024.
- ^ Enthought, Canopy. "Canopy". www.enthought.com. Archived from the original on 15 July 2017. Retrieved 20 August 2016.
- ^ "PEP 7 – Style Guide for C Code | peps.python.org". peps.python.org. Archived from the original on 24 April 2022. Retrieved 28 April 2022.
- ^ "4. Building C and C++ Extensions – Python 3.9.2 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 3 March 2021. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ van Rossum, Guido (5 June 2001). "PEP 7 – Style Guide for C Code". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 1 June 2020. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ "CPython byte code". Docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- ^ "Python 2.5 internals" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 August 2012. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ "Changelog – Python 3.9.0 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 7 February 2021. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- ^ "Download Python". Python.org. Archived from the original on 8 December 2020. Retrieved 13 December 2020.
- ^ "history [vmspython]". www.vmspython.org. Archived from the original on 2 December 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- ^ "An Interview with Guido van Rossum". Oreilly.com. Archived from the original on 16 July 2014. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ "Download Python for Other Platforms". Python.org. Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2020.
- ^ "PyPy compatibility". Pypy.org. Archived from the original on 6 June 2020. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ^ Team, The PyPy (28 December 2019). "Download and Install". PyPy. Archived from the original on 8 January 2022. Retrieved 8 January 2022.
- ^ "speed comparison between CPython and Pypy". Speed.pypy.org. Archived from the original on 10 May 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ^ "Codon: Differences with Python". Archived from the original on 25 May 2023. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ Lawson, Loraine (14 March 2023). "MIT-Created Compiler Speeds up Python Code". The New Stack. Archived from the original on 6 April 2023. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "Application-level Stackless features – PyPy 2.0.2 documentation". Doc.pypy.org. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ^ "Python-for-EV3". LEGO Education. Archived from the original on 7 June 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ^ Yegulalp, Serdar (29 October 2020). "Pyston returns from the dead to speed Python". InfoWorld. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ^ "cinder: Instagram's performance-oriented fork of CPython". GitHub. Archived from the original on 4 May 2021. Retrieved 4 May 2021.
- ^ Aroca, Rafael (7 August 2021). "Snek Lang: feels like Python on Arduinos". Yet Another Technology Blog. Archived from the original on 5 January 2024. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ Aufranc (CNXSoft), Jean-Luc (16 January 2020). "Snekboard Controls LEGO Power Functions with CircuitPython or Snek Programming Languages (Crowdfunding) – CNX Software". CNX Software – Embedded Systems News. Archived from the original on 5 January 2024. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ Kennedy (@mkennedy), Michael. "Ready to find out if you're git famous?". pythonbytes.fm. Archived from the original on 5 January 2024. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ Packard, Keith (20 December 2022). "The Snek Programming Language: A Python-inspired Embedded Computing Language" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 January 2024. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ "Plans for optimizing Python". Google Project Hosting. 15 December 2009. Archived from the original on 11 April 2016. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ "Python on the Nokia N900". Stochastic Geometry. 29 April 2010. Archived from the original on 20 June 2019. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- ^ "Brython". brython.info. Archived from the original on 3 August 2018. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ "Transcrypt – Python in the browser". transcrypt.org. Archived from the original on 19 August 2018. Retrieved 22 December 2020.
- ^ "Transcrypt: Anatomy of a Python to JavaScript Compiler". InfoQ. Archived from the original on 5 December 2020. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ "Nuitka Home | Nuitka Home". nuitka.net. Archived from the original on 30 May 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
- ^ Guelton, Serge; Brunet, Pierrick; Amini, Mehdi; Merlini, Adrien; Corbillon, Xavier; Raynaud, Alan (16 March 2015). "Pythran: enabling static optimization of scientific Python programs". Computational Science & Discovery. 8 (1). IOP Publishing: 014001. Bibcode:2015CS&D....8a4001G. doi:10.1088/1749-4680/8/1/014001. ISSN 1749-4699.
- ^ "The Python → 11l → C++ transpiler". Archived from the original on 24 September 2022. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ "google/grumpy". 10 April 2020. Archived from the original on 15 April 2020. Retrieved 25 March 2020 – via GitHub.
- ^ "Projects". opensource.google. Archived from the original on 24 April 2020. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- ^ Francisco, Thomas Claburn in San. "Google's Grumpy code makes Python Go". www.theregister.com. Archived from the original on 7 March 2021. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ "GitHub – IronLanguages/ironpython3: Implementation of Python 3.x for .NET Framework that is built on top of the Dynamic Language Runtime". GitHub. Archived from the original on 28 September 2021.
- ^ "IronPython.net /". ironpython.net. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021.
- ^ "Jython FAQ". www.jython.org. Archived from the original on 22 April 2021. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ Murri, Riccardo (2013). Performance of Python runtimes on a non-numeric scientific code. European Conference on Python in Science (EuroSciPy). arXiv:1404.6388. Bibcode:2014arXiv1404.6388M.
- ^ "The Computer Language Benchmarks Game". Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ^ a b Warsaw, Barry; Hylton, Jeremy; Goodger, David (13 June 2000). "PEP 1 – PEP Purpose and Guidelines". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 6 June 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ "PEP 8 – Style Guide for Python Code". Python.org. Archived from the original on 17 April 2019. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- ^ Cannon, Brett. "Guido, Some Guys, and a Mailing List: How Python is Developed". python.org. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 1 June 2009. Retrieved 27 June 2009.
- ^ "Moving Python's bugs to GitHub [LWN.net]". Archived from the original on 2 October 2022. Retrieved 2 October 2022.
- ^ "Python Developer's Guide – Python Developer's Guide". devguide.python.org. Archived from the original on 9 November 2020. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ^ Hughes, Owen (24 May 2021). "Programming languages: Why Python 4.0 might never arrive, according to its creator". TechRepublic. Archived from the original on 14 July 2022. Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- ^ "PEP 602 – Annual Release Cycle for Python". Python.org. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
- ^ "Changing the Python release cadence [LWN.net]". lwn.net. Archived from the original on 6 November 2019. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
- ^ Norwitz, Neal (8 April 2002). "[Python-Dev] Release Schedules (was Stability & change)". Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 27 June 2009.
- ^ a b Aahz; Baxter, Anthony (15 March 2001). "PEP 6 – Bug Fix Releases". Python Enhancement Proposals. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 27 June 2009.
- ^ "Python Buildbot". Python Developer's Guide. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ "1. Extending Python with C or C++ – Python 3.9.1 documentation". docs.python.org. Archived from the original on 23 June 2020. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ^ "PEP 623 – Remove wstr from Unicode". Python.org. Archived from the original on 5 March 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ^ "PEP 634 – Structural Pattern Matching: Specification". Python.org. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ^ "Documentation Tools". Python.org. Archived from the original on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ a b "Whetting Your Appetite". The Python Tutorial. Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 26 October 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- ^ "In Python, should I use else after a return in an if block?". Stack Overflow. Stack Exchange. 17 February 2011. Archived from the original on 20 June 2019. Retrieved 6 May 2011.
- ^ Lutz, Mark (2009). Learning Python: Powerful Object-Oriented Programming. O'Reilly Media, Inc. p. 17. ISBN 9781449379322. Archived from the original on 17 July 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2017.
- ^ Fehily, Chris (2002). Python. Peachpit Press. p. xv. ISBN 9780201748840. Archived from the original on 17 July 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2017.
- ^ Lubanovic, Bill (2014). Introducing Python. Sebastopol, CA : O'Reilly Media. p. 305. ISBN 978-1-4493-5936-2. Retrieved 31 July 2023.
- ^ Blake, Troy (18 January 2021). "TIOBE Index for January 2021". Technology News and Information by SeniorDBA. Archived from the original on 21 March 2021. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ^ "Quotes about Python". Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 3 June 2020. Retrieved 8 January 2012.
- ^ "Organizations Using Python". Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 21 August 2018. Retrieved 15 January 2009.
- ^ "Python : the holy grail of programming". CERN Bulletin (31/2006). CERN Publications. 31 July 2006. Archived from the original on 15 January 2013. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ^ Shafer, Daniel G. (17 January 2003). "Python Streamlines Space Shuttle Mission Design". Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ "Tornado: Facebook's Real-Time Web Framework for Python – Facebook for Developers". Facebook for Developers. Archived from the original on 19 February 2019. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- ^ "What Powers Instagram: Hundreds of Instances, Dozens of Technologies". Instagram Engineering. 11 December 2016. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- ^ "How we use Python at Spotify". Spotify Labs. 20 March 2013. Archived from the original on 10 June 2020. Retrieved 25 July 2018.
- ^ Fortenberry, Tim (17 January 2003). "Industrial Light & Magic Runs on Python". Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 6 June 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ^ Taft, Darryl K. (5 March 2007). "Python Slithers into Systems". eWeek.com. Ziff Davis Holdings. Archived from the original on 13 August 2021. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ GitHub – reddit-archive/reddit: historical code from reddit.com., The Reddit Archives, archived from the original on 1 June 2020, retrieved 20 March 2019
- ^ "Real time communication at scale with Elixir at Discord". 8 October 2020.
- ^ "What Programming Language is Baidu Built In?". 5 July 2018.
- ^ "Usage statistics and market share of Python for websites". 2012. Archived from the original on 13 August 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Oliphant, Travis (2007). "Python for Scientific Computing". Computing in Science and Engineering. 9 (3): 10–20. Bibcode:2007CSE.....9c..10O. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.474.6460. doi:10.1109/MCSE.2007.58. ISSN 1521-9615. S2CID 206457124. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- ^ Millman, K. Jarrod; Aivazis, Michael (2011). "Python for Scientists and Engineers". Computing in Science and Engineering. 13 (2): 9–12. Bibcode:2011CSE....13b...9M. doi:10.1109/MCSE.2011.36. Archived from the original on 19 February 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2014.
- ^ Science education with SageMath, Innovative Computing in Science Education, archived from the original on 15 June 2020, retrieved 22 April 2019
- ^ "OpenCV: OpenCV-Python Tutorials". docs.opencv.org. Archived from the original on 23 September 2020. Retrieved 14 September 2020.
- ^ Dean, Jeff; Monga, Rajat; et al. (9 November 2015). "TensorFlow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous systems" (PDF). TensorFlow.org. Google Research. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 November 2015. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- ^ Piatetsky, Gregory. "Python eats away at R: Top Software for Analytics, Data Science, Machine Learning in 2018: Trends and Analysis". KDnuggets. Archived from the original on 15 November 2019. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- ^ "Who is using scikit-learn? – scikit-learn 0.20.1 documentation". scikit-learn.org. Archived from the original on 6 May 2020. Retrieved 30 November 2018.
- ^ Jouppi, Norm. "Google supercharges machine learning tasks with TPU custom chip". Google Cloud Platform Blog. Archived from the original on 18 May 2016. Retrieved 19 May 2016.
- ^ De Raedt, Luc; Kimmig, Angelika (2015). "Probabilistic (logic) programming concepts". Machine Learning. 100 (1): 5–47. doi:10.1007/s10994-015-5494-z. S2CID 3166992.
- ^ "Natural Language Toolkit – NLTK 3.5b1 documentation". www.nltk.org. Archived from the original on 13 June 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ^ Andersen, C. and Swift, T., 2023. The Janus System: a bridge to new prolog applications. In Prolog: The Next 50 Years (pp. 93–104). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
- ^ "SWI-Prolog Python interface". Archived from the original on 15 March 2024. Retrieved 15 March 2024.
- ^ Tarau, P., 2023. Reflections on automation, learnability and expressiveness in logic-based programming languages. In Prolog: The Next 50 Years (pp. 359–371). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
- ^ "Tkinter — Python interface to TCL/Tk". Archived from the original on 18 October 2012. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- ^ "Python Tkinter Tutorial". 3 June 2020. Archived from the original on 9 June 2023. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- ^ "Installers for GIMP for Windows – Frequently Asked Questions". 26 July 2013. Archived from the original on 17 July 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- ^ "jasc psp9components". Archived from the original on 19 March 2008.
- ^ "About getting started with writing geoprocessing scripts". ArcGIS Desktop Help 9.2. Environmental Systems Research Institute. 17 November 2006. Archived from the original on 5 June 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ^ CCP porkbelly (24 August 2010). "Stackless Python 2.7". EVE Community Dev Blogs. CCP Games. Archived from the original on 11 January 2014. Retrieved 11 January 2014.
As you may know, EVE has at its core the programming language known as Stackless Python.
- ^ Caudill, Barry (20 September 2005). "Modding Sid Meier's Civilization IV". Sid Meier's Civilization IV Developer Blog. Firaxis Games. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010.
we created three levels of tools ... The next level offers Python and XML support, letting modders with more experience manipulate the game world and everything in it.
- ^ "Python Language Guide (v1.0)". Google Documents List Data API v1.0. Archived from the original on 15 July 2010.
- ^ "Python Setup and Usage". Python Software Foundation. Archived from the original on 17 June 2020. Retrieved 10 January 2020.
- ^ "Immunity: Knowing You're Secure". Archived from the original on 16 February 2009.
- ^ "Core Security". Core Security. Archived from the original on 9 June 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ^ "What is Sugar?". Sugar Labs. Archived from the original on 9 January 2009. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ^ "4.0 New Features and Fixes". LibreOffice.org. The Document Foundation. 2013. Archived from the original on 9 February 2014. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- ^ "Gotchas for Python Users". boo.codehaus.org. Codehaus Foundation. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ Esterbrook, Charles. "Acknowledgements". cobra-language.com. Cobra Language. Archived from the original on 8 February 2008. Retrieved 7 April 2010.
- ^ "Proposals: iterators and generators [ES4 Wiki]". wiki.ecmascript.org. Archived from the original on 20 October 2007. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ "Frequently asked questions". Godot Engine documentation. Archived from the original on 28 April 2021. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- ^ Kincaid, Jason (10 November 2009). "Google's Go: A New Programming Language That's Python Meets C++". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on 18 January 2010. Retrieved 29 January 2010.
- ^ Strachan, James (29 August 2003). "Groovy – the birth of a new dynamic language for the Java platform". Archived from the original on 5 April 2007. Retrieved 11 June 2007.
- ^ "Modular Docs – Why Mojo". docs.modular.com. Archived from the original on 5 May 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
Mojo as a member of the Python family [..] Embracing Python massively simplifies our design efforts, because most of the syntax is already specified. [..] we decided that the right long-term goal for Mojo is to provide a superset of Python (i.e. be compatible with existing programs) and to embrace the CPython immediately for long-tail ecosystem enablement. To a Python programmer, we expect and hope that Mojo will be immediately familiar, while also providing new tools for developing systems-level code that enable you to do things that Python falls back to C and C++ for.
- ^ Spencer, Michael (4 May 2023). "What is Mojo Programming Language?". datasciencelearningcenter.substack.com. Archived from the original on 5 May 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ Yegulalp, Serdar (16 January 2017). "Nim language draws from best of Python, Rust, Go, and Lisp". InfoWorld. Archived from the original on 13 October 2018. Retrieved 7 June 2020.
Nim's syntax is strongly reminiscent of Python's, as it uses indented code blocks and some of the same syntax (such as the way if/elif/then/else blocks are constructed).
- ^ "An Interview with the Creator of Ruby". Linuxdevcenter.com. Archived from the original on 28 April 2018. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ^ Lattner, Chris (3 June 2014). "Chris Lattner's Homepage". Chris Lattner. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2014.
I started work on the Swift Programming Language in July of 2010. I implemented much of the basic language structure, with only a few people knowing of its existence. A few other (amazing) people started contributing in earnest late in 2011, and it became a major focus for the Apple Developer Tools group in July 2013 [...] drawing ideas from Objective-C, Rust, Haskell, Ruby, Python, C#, CLU, and far too many others to list.
- ^ Jalan, Nishant Aanjaney (10 November 2022). "Programming in Kotlin". CodeX. Retrieved 29 April 2024.
- ^ Kupries, Andreas; Fellows, Donal K. (14 September 2000). "TIP #3: TIP Format". tcl.tk. Tcl Developer Xchange. Archived from the original on 13 July 2017. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ^ Gustafsson, Per; Niskanen, Raimo (29 January 2007). "EEP 1: EEP Purpose and Guidelines". erlang.org. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ "Swift Evolution Process". Swift Programming Language Evolution repository on GitHub. 18 February 2020. Archived from the original on 27 April 2020. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
Sources
[edit]- "Python for Artificial Intelligence". Python Wiki. 19 July 2012. Archived from the original on 1 November 2012. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- Paine, Jocelyn, ed. (August 2005). "AI in Python". AI Expert Newsletter. Amzi!. Archived from the original on 26 March 2012. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- "PyAIML 0.8.5 : Python Package Index". Pypi.python.org. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- Russell, Stuart J. & Norvig, Peter (2009). Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-604259-4.
Further reading
[edit]- Downey, Allen B. (May 2012). Think Python: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist (version 1.6.6 ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-72596-5.
- Hamilton, Naomi (5 August 2008). "The A-Z of Programming Languages: Python". Computerworld. Archived from the original on 29 December 2008. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
- Lutz, Mark (2013). Learning Python (5th ed.). O'Reilly Media. ISBN 978-0-596-15806-4.
- Summerfield, Mark (2009). Programming in Python 3 (2nd ed.). Addison-Wesley Professional. ISBN 978-0-321-68056-3.
- Ramalho, Luciano (May 2022). Fluent Python. O'Reilly Media. ISBN 978-1-4920-5632-4.
External links
[edit]- Python (programming language)
- Class-based programming languages
- Notebook interface
- Computer science in the Netherlands
- Concurrent programming languages
- Cross-platform free software
- Cross-platform software
- Dutch inventions
- Dynamically typed programming languages
- Educational programming languages
- High-level programming languages
- Information technology in the Netherlands
- Multi-paradigm programming languages
- Object-oriented programming languages
- Pattern matching programming languages
- Programming languages
- Programming languages created in 1991
- Scripting languages
- Text-oriented programming languages

